First of all, I should probably admit that, despite the title of this post, no, the redhat.corpmerchandise.com fiasco is not Mozilla’s fault: it’s Red Hat’s, because obviously Mozilla has no control over that domain. But that wouldn’t make for a very interesting title for a blog post, and Mozilla set the stage for this to happen, so let’s go with “Mozilla’s fault.” Also, it’s not really Red Hat’s fault; Staples is really to blame, since corpmerchandise.com is their domain, but I really shouldn’t be pointing that out when the point of this blog post is to blame Mozilla. And gosh now I’m off on a tangent, but it’s not really a fiasco either: it’s a significant screw-up, but not that big a deal; but words like “fiasco” make for good clickbait headlines, so let’s go with that. FIASCO.
One last note before I begin. I hold Mozilla to a higher standard than other software development companies. Sometimes it makes mistakes, like the one I’m about to present, and it’s important to call them out when this happens, but it’s because of good choices at Mozilla that Firefox still (mostly) respects your freedom, unlike other major browsers. It’s a good company.
OK, so you’ve read this far in suspense, I should probably explain the redhat.corpmerchandise.com fiasco before you reach the end of your three-paragraph Internet-length attention span. Yesterday the Fedora Store went live, where you can buy low-cost Fedora-branded items: a T-shirt, water bottle, pub glass, or baseball cap. I want a T-shirt. OK, that’s great, so what is the fiasco? Well click on this link (quick! before it gets fixed!) to find out: https://redhat.corpmerchandise.com/ProductList.aspx?did=20588
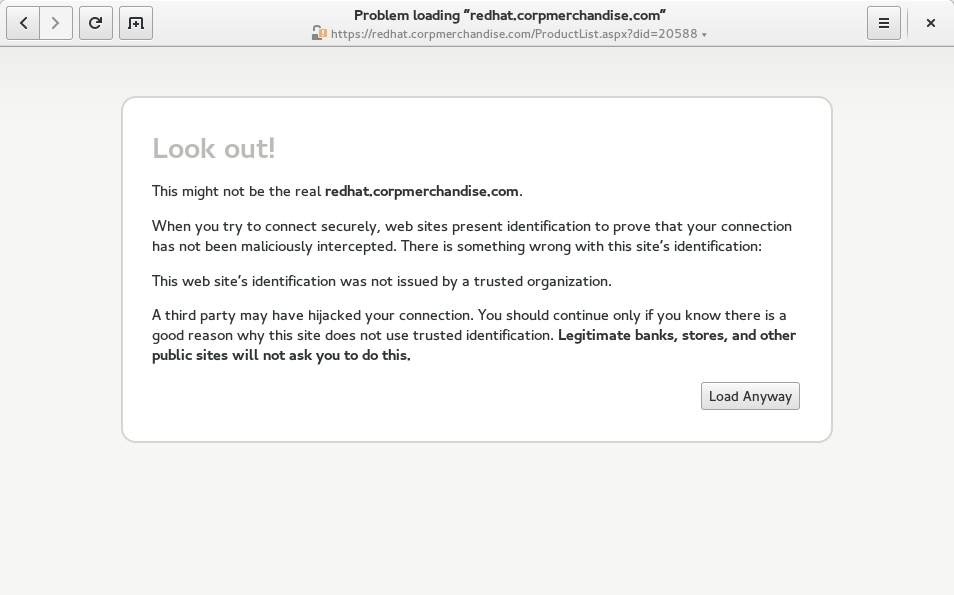
Now, depending on your browser, you may or may not have discovered the problem. When I load that site in Firefox, I see Fedora merchandise. When I load it in Epiphany, I see something noticeably less friendly:
“Legitimate banks, stores, and other public sites will not ask you to do this.” Ouch. (I actually took that language from Firefox when I designed that interstitial for Epiphany.) Ah, well, clearly there is some bug in Epiphany, because Firefox is a major browser and Firefox doesn’t get stuff like this wrong, right? Well, no, Epiphany is not wrong. Then Firefox is wrong? Well… from a certain point of view… (like mine)….
Firefox and Epiphany use different cryptography libraries to determine if the certificate is valid, and they sometimes differ in what certificates they will accept. Firefox uses NSS, a library maintained by Mozilla primarily for use by Firefox (it’s also used by Chrome on Linux), while Epiphany (indirectly) uses GnuTLS, originally a GNU project that is now de-facto maintained by Red Hat. So is NSS just better than GnuTLS at determining whether a certificate is valid? Actually, NSS really is more permissive than GnuTLS, and this does sometimes lead Firefox to approve of sites that Epiphany will not, but that’s not the case here. Let’s try a little experiment to see what’s happening. Firefox has a weird feature that feels like it was designed in the 90s for the era when computers had one user account apiece: it lets you create multiple profiles for bookmarks, history, and other settings. So let’s give this a whirl:
$ firefox -ProfileManager
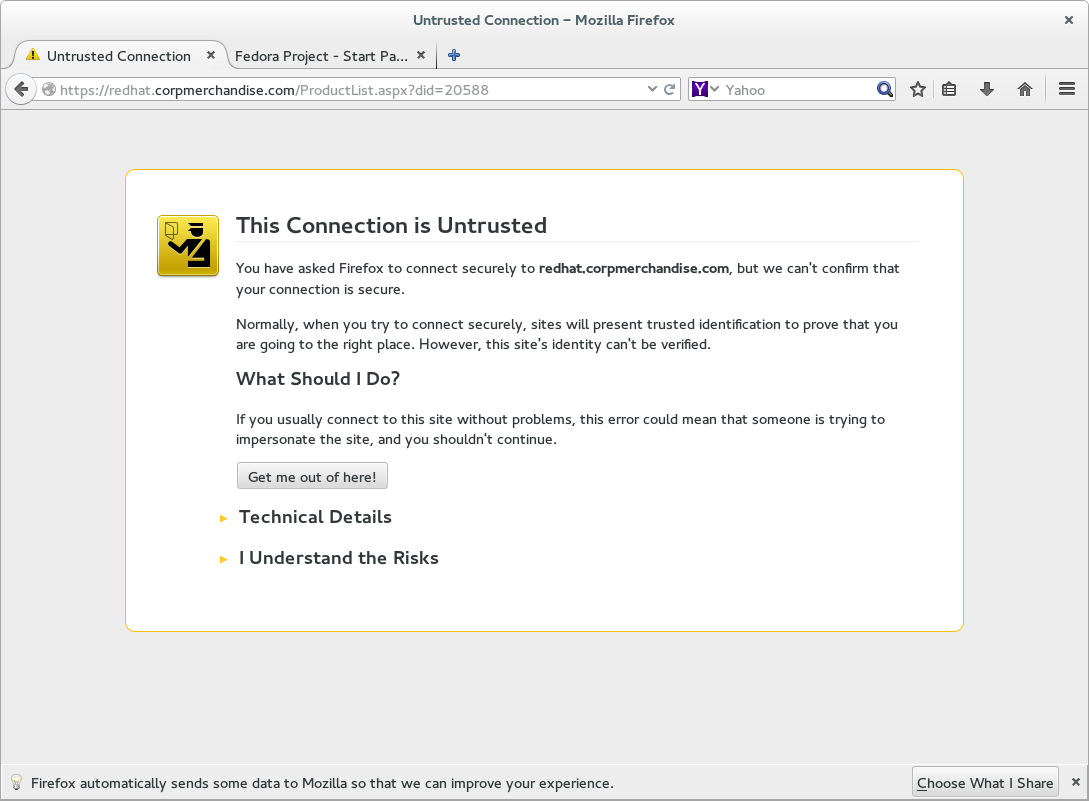
Create a new profile, launch Firefox with it, then load https://redhat.corpmerchandise.com/ProductList.aspx?did=20588 to try this experiment again. Or just keep reading and trust me when I say that you’ll see this:
Oooh, that’s not good, now Firefox thinks we’re being attacked. We’re not. So what’s going on here? Why is Firefox so inconsistent?
First off, let’s get one thing straight: this site is totally and hopelessly broken. To see why, let’s use the super-handly tool gnutls-cli:
$ gnutls-cli redhat.corpmerchandise.com
Processed 182 CA certificate(s).
Resolving 'redhat.corpmerchandise.com'...
Connecting to '174.47.191.32:443'...
- Certificate type: X.509
- Got a certificate list of 1 certificates.
- Certificate[0] info:
- subject `C=US,ST=Kansas,L=Overland Park,O=STAPLES CONTRACT & COMMERCIAL\, INC.,OU=Information Techology,CN=*.corpmerchandise.com', issuer `C=US,O=DigiCert Inc,OU=www.digicert.com,CN=DigiCert SHA2 High Assurance Server CA', RSA key 2048 bits, signed using RSA-SHA256, activated `2014-11-12 00:00:00 UTC', expires `2015-12-09 12:00:00 UTC', SHA-1 fingerprint `50cfb26c680434d132dc64e80db54de51a5a07a6'
Public Key ID:
c273ca58bfdb2902ea30dbf5946c27178affd588
Public key's random art:
+--[ RSA 2048]----+
| |
| |
| |
| . |
| = S |
| .* O o o |
|o .+.X E o . |
| =.. =.+.+ . |
|..o oo+oo |
+-----------------+
- Status: The certificate is NOT trusted. The certificate issuer is unknown.
*** PKI verification of server certificate failed...
*** Fatal error: Error in the certificate.
*** Handshake has failed
GnuTLS error: Error in the certificate.
If you’re familiar with digital certificates, it’s pretty obvious what’s wrong here. When you connect securely to a web site, it sends a chain of certificates: the first certificate is owned by the web site, then it sends some number of additional certificates, usually one or two, that belong to certificate authorities. Each certificate is signed by the next certificate in the chain (not quite, but it’s almost true, so let’s go with that for this post), up until you get to the last one in the chain, which must be signed by a certificate in your browser’s (or operating system’s) root trust store. The certificates in your root trust store are super valuable, and if one were to be compromised by an attacker the devastation to the Web would be terrible, so certificate authorities must keep their roots safe at all costs, and they do this by almost never using them. Legitimate certificate authorities never sign web sites’ certificates with their root certificate; instead, they create a few other certificates, sign them with the root, and use only those to sign web sites’ certificates. So if you ever visit a site and it sends you only one certificate, you know that the site is broken for sure. And here we have a site that has sent only one certificate (there’s a Certificate[0] but no Certificate[1]), a classic case of server misconfiguration (aka fiasco).
So why did Firefox allow the site at first, even though it has no chain of trust, but not allow it with a fresh profile? Well, even though the site has presented no chain of trust, NSS goes far, far out of its way to find one. Whenever you visit a web site, NSS saves each intermediate certificate it sees, makes sure it’s signed by a trusted root, and caches it for future use. Then, whenever you visit a site that sends a broken chain of trust, NSS will effectively treat all those intermediates as roots, and use them to complete the chain of trust. This is completely safe, since it has already verified them. Those intermediate certs are saved in your Firefox profile, so by switching to a fresh profile they are no longer used, and you can’t access the broken site anymore.
If you were able to access redhat.corpmerchanise.com in Firefox, you can verify this for yourself: open Preferences -> Advanced -> Certificates -> View Certificates -> Authorities. Anything listed as Default Trust or System Trust is a root, and anything listed as Software Security Device is a cached intermediate cert. Don’t touch those root certs, but feel free to Delete or Distrust any Software Security Device — it will just be cached again the next time you visit a web site that uses it. Scroll down to DigiCert SHA2 High Assurance Server CA. That’s the cached intermediate cert that is allowing you to visit redhat.corpmerchandise.com — it’s not shipped with Firefox, and new Firefox users won’t have it. Delete it, restart the browser, then try reloading https://redhat.corpmerchandise.com. Oh no, it’s untrusted! Now visit https://stackoverflow.com, which sends a certificate signed by DigiCert SHA2 High Assurance Server CA, which will cause NSS to cache it once again. Now back to https://redhat.corpmerchandise.com, and Firefox knows it’s safe again. And that, folks, is how you screw up your web site so that it only works if you first visit Stack Overflow.
So why does NSS do this? Well, once upon a time (ten years ago), browsers were less strict about verifying chains of trust, and on an untrusted connection would let you proceed with maybe just a pop-up warning, and maybe not even that. So sites were less diligent about making sure they had valid chains of trust than they are today, in the era of nasty interstitial warnings that discourage the user from visiting the site. Since there were a lot of sites with broken chains, NSS chose to cache intermediate certificates to reduce the number of unnecessary validation errors for Firefox users. At the time, this might have been an OK choice.
Today, if your online store is missing a chain of trust, the browser makes clear in no uncertain terms that this site is not to be trusted, and sites lose visitors/customers, so they try pretty hard to get this right. (How many lost visitors depends on the browser — a large majority of Chrome and probably Epiphany users will click through the warnings, but a large majority of Firefox users will not, because Firefox’s UI for this is much scarier.) When setting up a new site, you check it in a couple of browsers to make sure it works properly, and you trust that if it works in Firefox on your machine, surely it will work in Firefox for everyone else, right? Well, no, it won’t. When setting up a secure web site, you must always test it with a fresh Firefox profile to make sure that you got the chain of trust correct. Of course, nobody knows to do this, which is how we wind up with broken sites like redhat.corpmerchandise.com.
I suspect this breakage would happen far less often if NSS did not cache intermediate certs, tricking site admins into thinking their sites are set up properly. Sure, cached certs don’t hurt the user who has them cached, but they’re bad for all other users of Firefox, as well as users of browsers that do no certificate caching. And there’s no good reason for this, because browsers don’t need to cache intermediate certificates in 2015, because almost all sites that redirect from HTTP to HTTPS get this right nowadays, and those that get it wrong are probably getting it wrong because they tested with a browser that had the right cached intermediate. Chicken and egg much? There’s only one way to fix this problem, and that brings me to my request: Mozilla, do the Web a favor and stop caching intermediate certificates.
P.S. Astute readers would note that there’s absolutely no point in deleting an intermediate certificate with the Firefox certificate manager, except to test things like this. It’s just going to come back the next time you see it.