GNOME Shell
Unified Layout for Dialogs
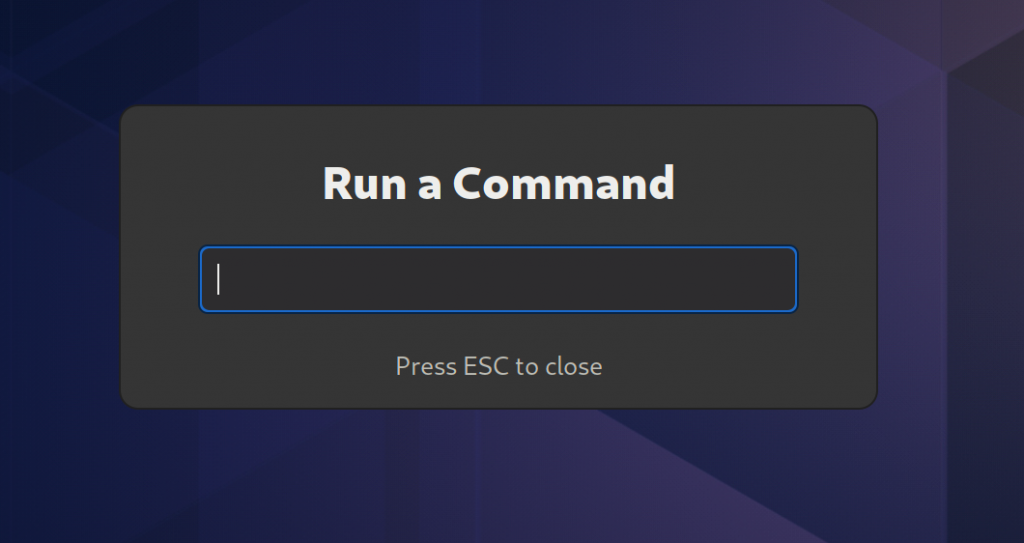
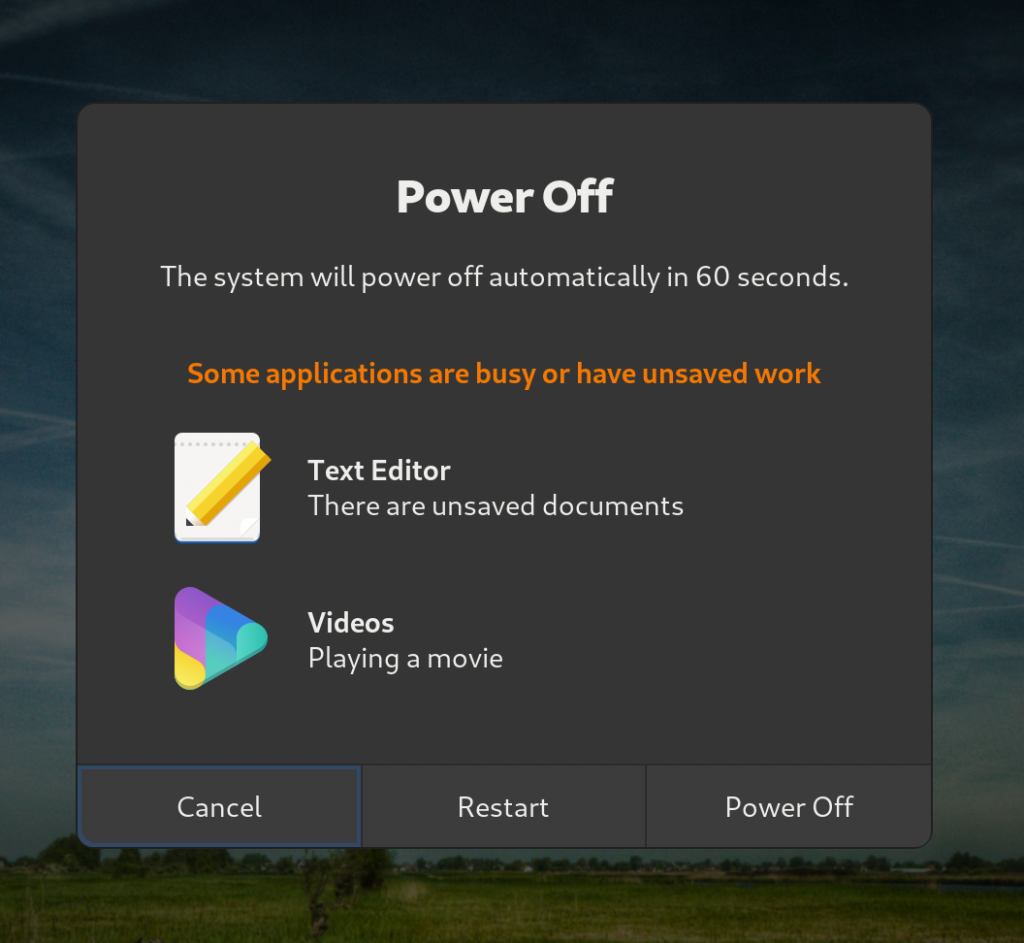
One area of focus during this cycle was unifying the layout, content structure, and feel of dialogs in GNOME Shell. Many dialogs were redesigned, polished, and updated as a result of this effort:
Improved Gesture Support
The gestures to switch workspaces, and navigate through the application grid pages, were dramatically improved, and now follow the touchpad movement.
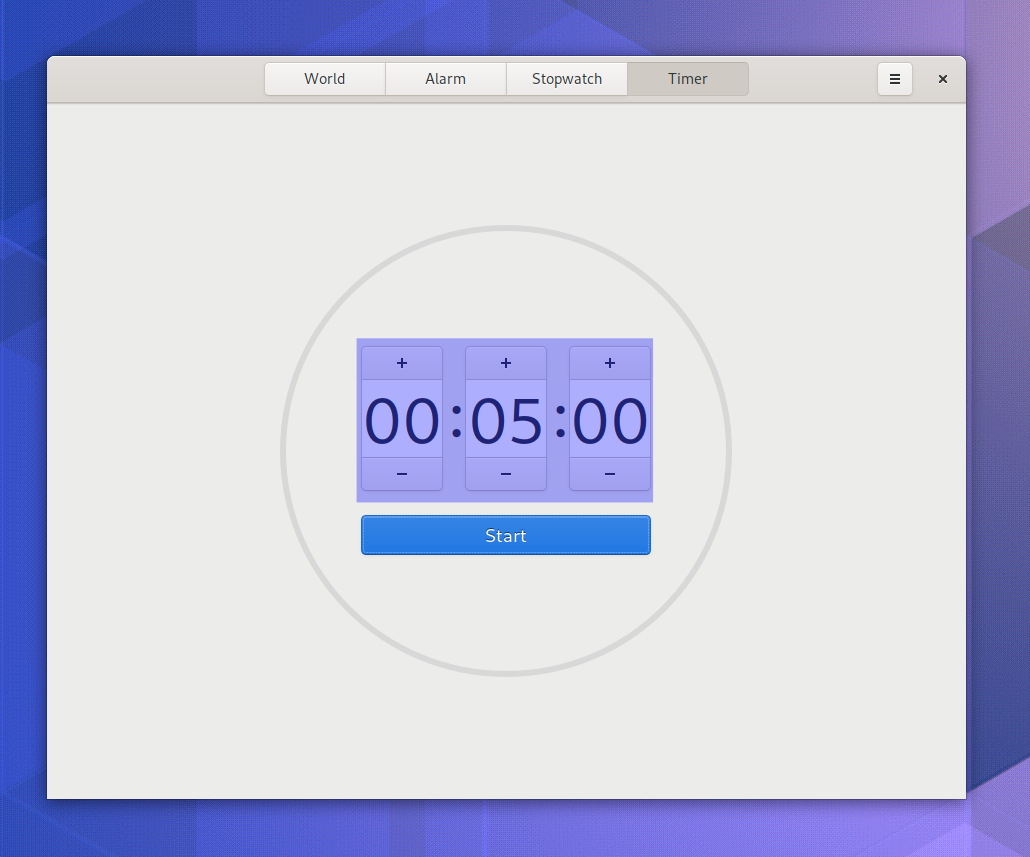
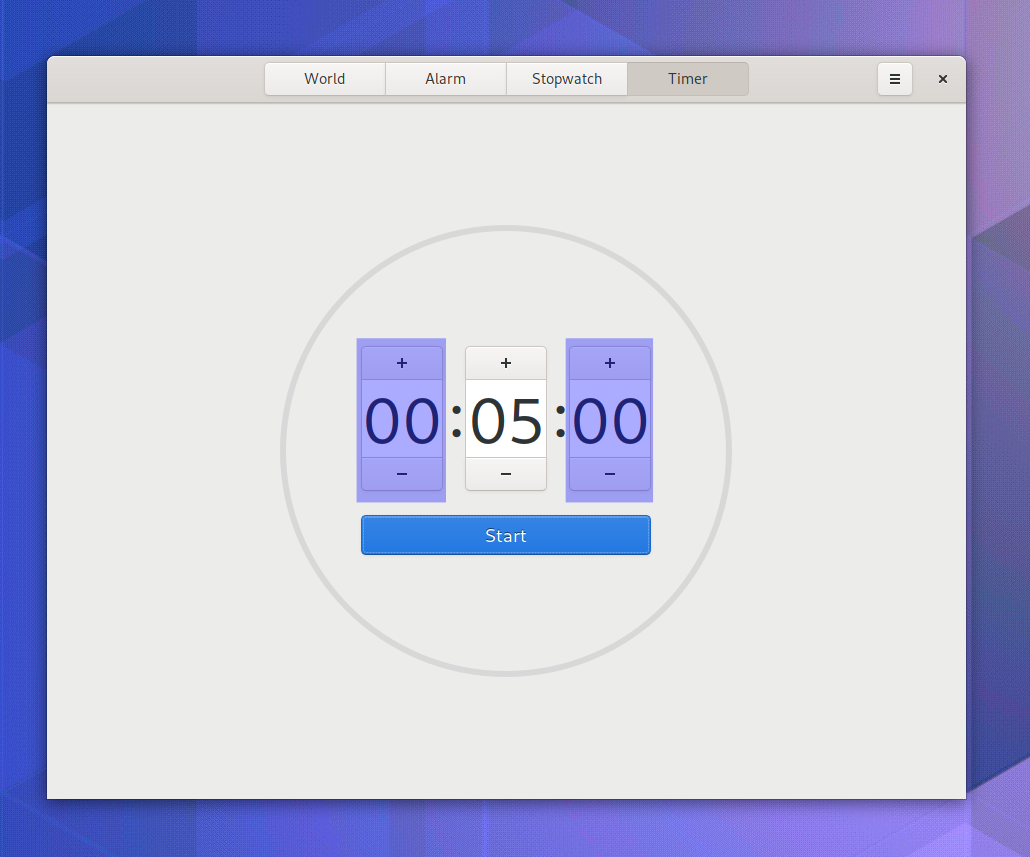
Password Peek
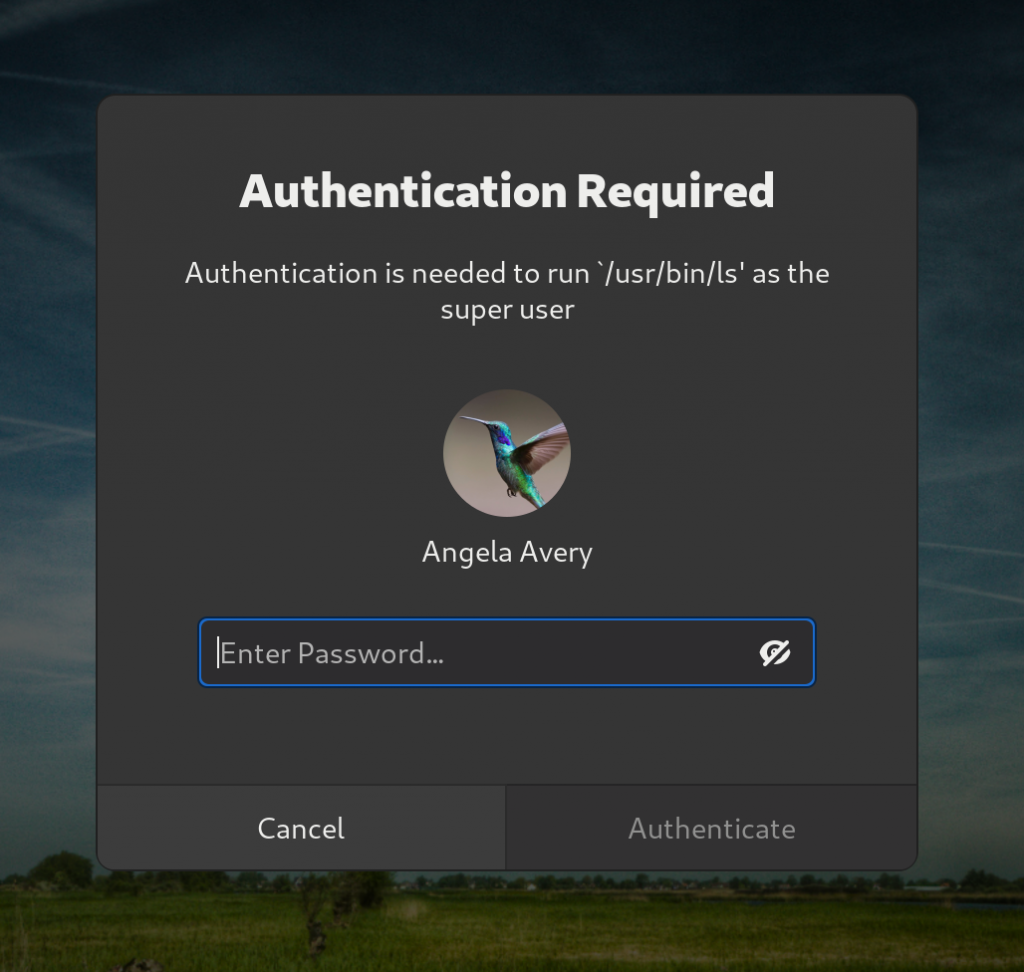
The password entries in GNOME Shell now support peeking passwords! Take a look:
Folders as Dialogs
A major change on how GNOME Shell handles application folders has landed this month. Instead of being displayed as popups within the application grid, folders are now displayed above it in the form of a dialog.
Miscellaneous
A new blur effect was added to GNOME Shell. It will be used by future work, such as a redesigned lock screen, among others.
Due to the VP9 encoder being too CPU-intensive, the built-in screen recorder changed back to the VP8 encoder.
As part of a code refactoring effort, the bits of StBoxLayout that deal with hiding overflowing content were moved to a new class, StViewport. This simplifies in various ways the implementation of overflowed content in GNOME Shell.
When managing the icons in the application grid, such as creating, renaming, or deleting folders, or moving app icons in and out of these folders, the icons will animate to their positions smoothly now.
GNOME Shell’s performance profiling framework was fixed and updated to also work on Wayland.
The SCSS code that is used to generate the default GNOME Shell theme was completely revamped and reorganized, making it easier to find specific theme classes. It also received a small visual update.
At last, GNOME Shell now supports NVidia GPU offloading by showing the “Launch on Discrete GPU” entry on systems with a NVidia discrete GPU available.
Mutter
More Cogl Cleanups
Cogl is the GPU rendering abstraction used by Clutter to render its contents on screen. Clutter itself is the base of Mutter and GNOME Shell, which add window management and compositing on top of Clutter.
During the past few months, there were continued efforts to cleanup and modernize Cogl by removing dead and unused code, using more modern OpenGL features, etc.
This work continued during December and January too, with more dead code saying goodbye, and more modern code being welcomed to the codebase.
Implicit Cogl API Removal
Due to historical reasons, Cogl has two major APIs: an explicit one, with properly defined types, and functions that receive the objects they should act on; and an implicit one, that is closer to the OpenGL model, and acts on an implicit state machine with the objects to be worked on.
Many parts of the Clutter, Mutter, and GNOME Shell codebases were using the implicit Cogl API. Those usages were updated, and allowed us to remove most of the implicit API from Cogl.
ClutterOffscreenEffect Improvements
ClutterOffscreenEffect is an effect applied on UI elements that allow them to be rendered in offscreen framebuffers. This allows interesting, shader-based effects to be applied to these elements, such as contrast and brightness, blur, among others.
A few bugs were found in this effect, and were ironed out. It also received some optimizations that allow the effect to release GPU memory more often.
Introduction of ClutterSeat
Clutter’s representation of input devices was designed in the X11/XI2 times, and the API was modeled after it. This change brings the internal input model closer to Wayland.
While it may sound an unimpressive change, it’s the cornerstone for an unification of the multiple input grabbing mechanisms in use by GNOME Shell.
Between other internal refactors that are now possible, it will also facilitate the introduction of an input thread in the native backend, so the pointer cursor is no longer frozen on stalls.
This will be covered in detail in a separate article.
Improve layout phase of no-layout actors
The Clutter toolkit follows the traditional rendering pipeline, composed of the layout, paint, and pick phases. The layout phase is where the elements (in Clutter terminology, “actors”) get to know their position and size; the paint phase is where these actors paint their contents on the framebuffer; and the pick phase is where Clutter figures out which actor is hovered by the pointer.
When we know beforehand that an actor is not going to move around the screen, we can tell Clutter about it, and the layout phase can be optimized to avoid some calculations. This mode is called “no-layout”.
During January, Clutter received another set of optimizations when dealing with no-layout actors. This can reduce CPU use on some specific scenarios, such as when dragging windows.
Miscellaneous
The ClutterContent interface now is better integrated in the size negotiation phase of ClutterActors, by making actors that follow their content’s sizes report their content’s geometry.
Many improvements to how Mutter tracks Wayland windows landed. Specifically, a crasher related to wl_subsurface was ironed out, a unit test framework was introduced, and a harmless runtime warning was fixed.
When dealing with multi-GPU setups, Mutter needs to share framebuffers across GPUs. There are currently three ways to do that:
- The secondary GPU does an accelerated copy of the primary GPU framebuffer;
- The primary GPU does an accelerated copy of its own contents to the secondary GPU framebuffer;
- A slow, non-accelerated framebuffer is created on the secondary GPU, mapped to CPU memory, and the primary GPU contents are copied to this memory;
Mutter now features an additional way to share framebuffers: the primary GPU exports a framebuffer that is imported and read directly by the secondary GPU. This method is useful with virtual secondary GPUs, such as DisplayLink docks.