A couple of weeks ago I asked people to run a command which uploaded all their auto-EDID display profiles to me. This was a massive success with 1858 profiles being added to a large dataset. These were scanned by the cd-find-broken tool, and results plotted on my G+ page. As there’s been so much new data I’m updating the graphs:
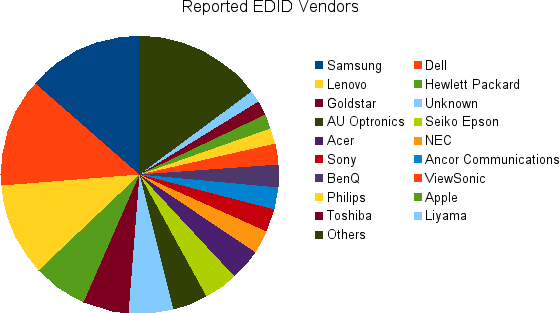
I’m actually using this data to make sure we show something sane in the client UIs. Some interesting vendors are not included, e.g.:
- “System manufacturer”,3
- “To Be Filled By O.E.M.”,4
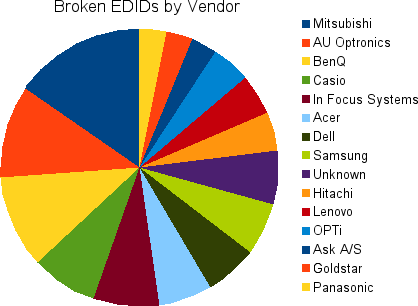
This is a chart of vendors Doing It Wrong™ by including random data (or implausible data) as the display primaries.
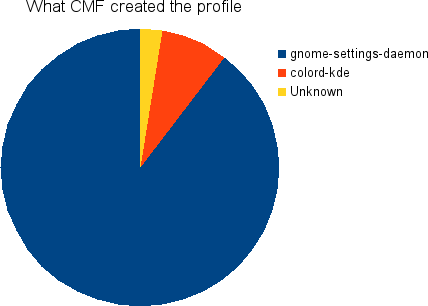
This shows what program created the Auto-EDID ICC profile. Unknown is probably a mixture of oyranos and also early versions of gnome-setting-daemon which didn’t set the extra metadata.
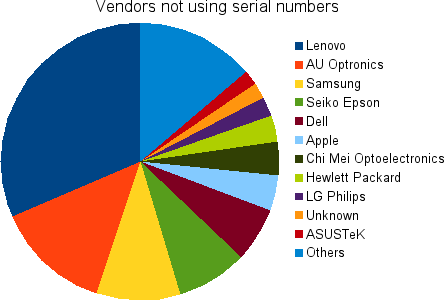
Last graph I promise. This shows a chart of all the vendors who do not populate the serial number in the EDID blob. I’ll explain why this is bad.
When we construct the device ID for colord, we use the vendor{-model}{-serial} as part of the key. This allows you to use different ICC profiles even if you’ve got two “identical” external panels attached. Without the serial number, “lenovo-foo” looks the same as “lenovo-foo” and colord treats them as if they were the same panel. This sucks if the panels were not bought at the same time and have identical backlight burn time. Ohh, and we can’t use the connection name (e.g. DVI-1) as it would suck if you had to reassign all your profiles if you moved the connector to DVI-2…
This isn’t always a disaster: Laptops. We only need the make and model to ensure this is unique on the system as you can’t typically have two internal panels installed. This explains the Lenovo, Samsung, Dell and Apple entries I think, so don’t get out the pitchforks just yet. Unfortunately there’s nothing in the ICC profile that says “this is a laptop” so we can’t be more selective and hence this graph isn’t super useful. But, even on laptops, vendors should really be doing something semi-sane with the serial number, even if it’s just the batch number.
A new 0.1.34 colord was released this week. Thanks again to everyone that uploaded profiles.