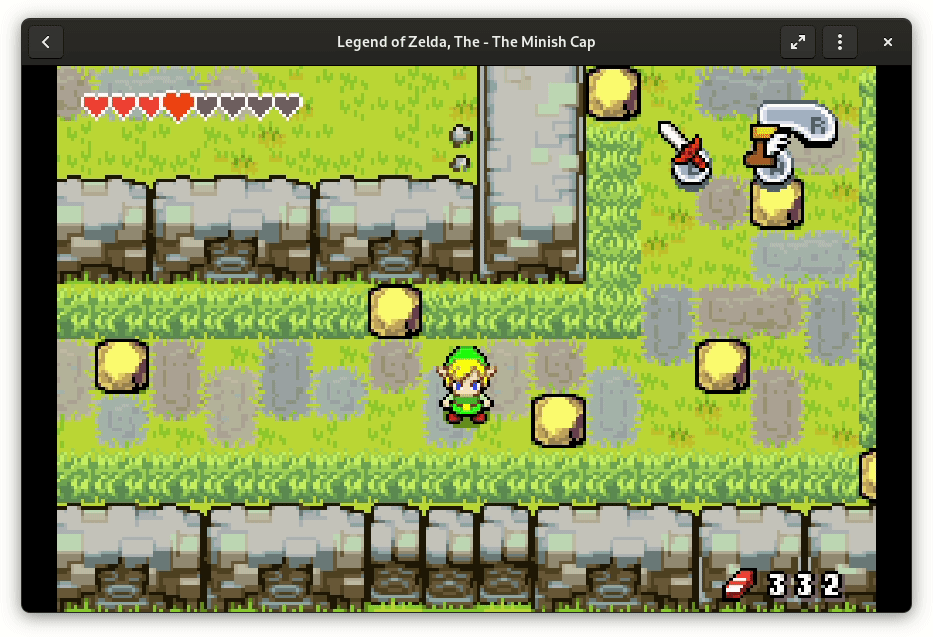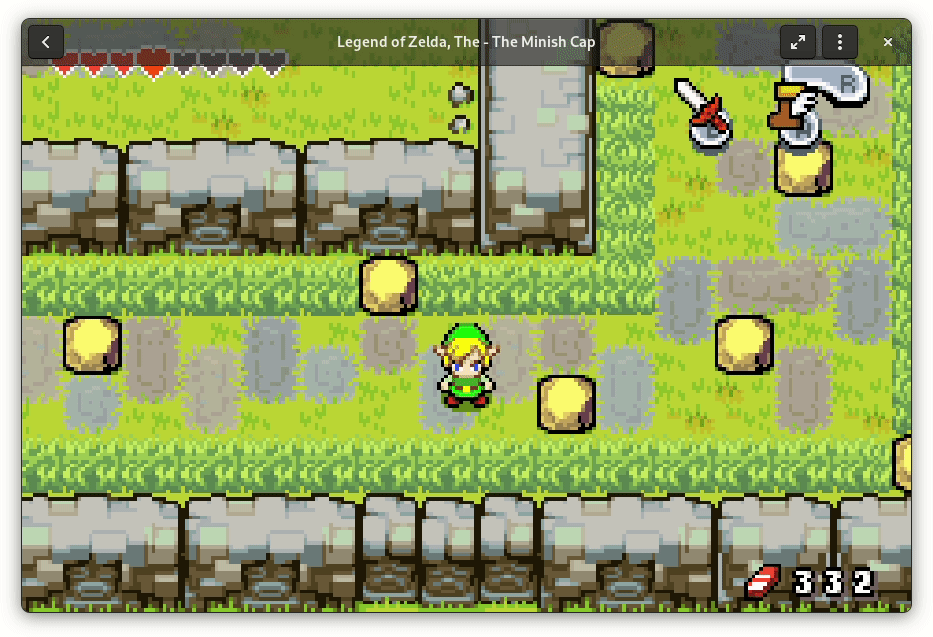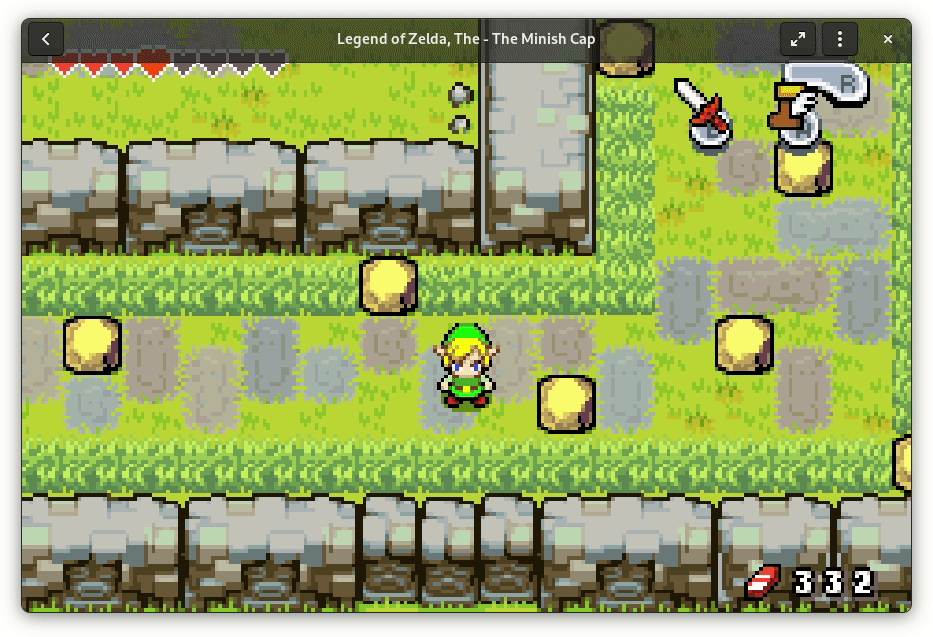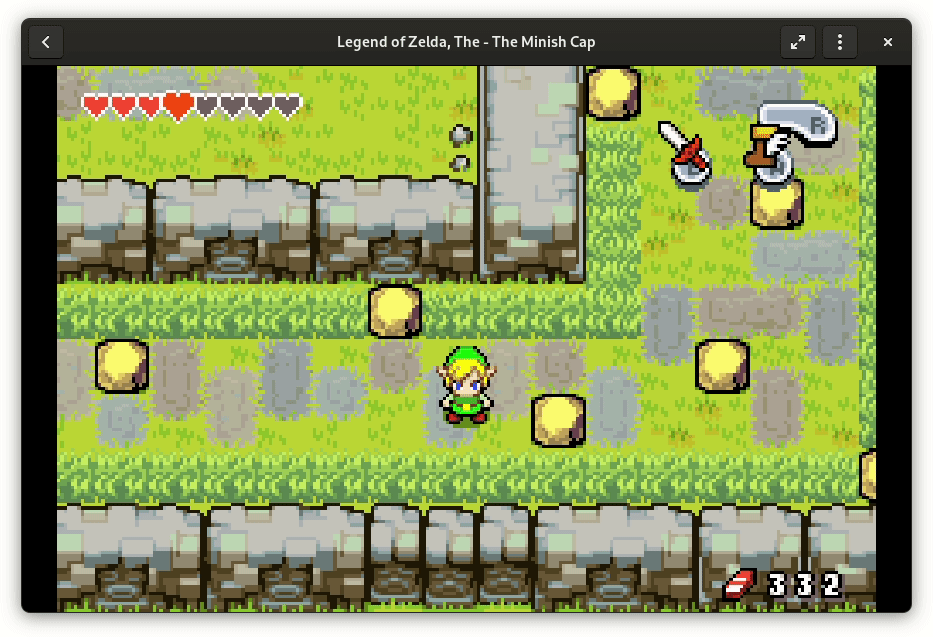
Recently, I’ve been working on a few widgets for libhandy to provide applications more flexibility with how to handle their titlebars.
But doesn’t GTK already allow this? Let’s take a look.
First, GTK has a widget called GtkHeaderBar. It looks like a titlebar, has a close button, a title, a subtitle and allows to add widgets at the left or right sides, or to replace title and subtitle with a custom widget.
Second, there’s gtk_window_set_titlebar() function that allows to set a widget as a custom titlebar. GTK will place that widget above the main window area, and then it can be dragged to move the window, and will handle right click menu, double click and middle click. Additionally, GTK will draw client-side window border and/or shadows and provide an area to resize the window with. Naturally, GtkHeaderBar is a perfect fit for it, although nothing is preventing other widgets from being titlebars.
If nothing is set, GtkWindow will use a GtkHeaderBar with a special style class (.default-decoration) as a titlebar on Wayland, or legacy decorations on X11.
This approach works well if an application just wants to have a titlebar with some widgets in it. However, in many cases it’s more complex. Let’s take a look at some cases that are difficult or impossible to implement right now.
Split headerbars

A very common case is for dual-pane applications to have a separate titlebar for each pane, also known as split headerbars. To do this, you have to create a horizontal box with the panes divided by a separator, and put it into the window. Then you create another box containing two headerbars and another separator, and set that box as a titlebar. Then you need to ensure the width of the headerbars matches the content panes, either by hardcoding it or using a horizontal GtkSizeGroup. And then there’s the whole problem of ensuring the window controls show up on the correct headerbars.
Fast forward to 2020, now we have libhandy and HdyLeaflet. Now instead of two boxes you use two leaflets, and now it’s necessary to use a GtkSizeGroup for each pane, to ensure the folding animation doesn’t go out of sync. For window controls libhandy provides HdyHeaderGroup, so at least that’s simple. Also, you wrap the titlebar leaflet into a HdyTitleBar.
And then leaflet gained support for back/forward swipe gestures. Since we have two leaflets, their swipe progress has to be synchronized via a HdySwipeGroup, so that brings the number of the helper “group” objects to four.
Stack navigation

Somewhat related, many applications have multiple views, with a separate GtkHeaderBar for each view. This includes the split headerbar case on mobile, where the two leaflets shows only one view at a time.
It’s implemented via GtkStack. One stack in the window has the views, and another stack in titlebar has headerbars, then you always change their visible child at the same time. libhandy 1.0 will have HdyDeck allowing back/forward swipes the same way HdyLeaflet does, and so the two decks must be synchronized via a HdySwipeGroup too.
Stack navigation and split headerbars can be combined, with some views having split headerbars, and others having just one headerbar. Either way, you have to duplicate the whole hierarchy between the window and titlebar and keep it in sync, however complex it might be.
In both cases you might want to animate the transition. With swipes it’s pretty much necessary. And doing that breaks the window corners during the transition.
libhandy has a workaround for that called HdyTitleBar. It’s a simple GtkBin subclass that looks like a headerbar. Combined with the fact Adwaita CSS specifies transparent background for any nested headerbars, it means you can put a stack/box/leaflet/deck/anything with headerbars into a HdyTitleBar and animate them without moving the background, working around the corners issue. It’s not perfect, as tall content (such as a separator) would still overlap the corners, but it works in most cases.
Autohiding headerbar
Some applications want to hide headerbar to focus on the content. The easiest way to do it is to fade out the headerbar and just have a blank space there.

Since the titlebar is a separate area from the window, there’s no content behind it, so fading it out leaves an unsightly blank area.
There are ways to mitigate that. For example, one could hide the titlebar widget completely. That’s what UberWriter, now Apostrophe, does in the latest development version:

It works, but the code is not pretty. It uses two headerbars: one in the titlebar area, another one in the window area in a GtkOverlay. To hide the titlebar, it immediately hides the headerbar in the titlebar area, then shows the headerbar inside the window and fades it out. Then it adds some CSS to add round corners on the window instead of headerbar, and makes sure nothing overlaps them. Oh, and it also shifts the scroll position so that the text doesn’t jump.
Another way is to use a revealer with a slide transition inside the headerbar area. Then it’s possible to shift scroll position on each frame of the transition, although it leads to a visual glitch with window corners.
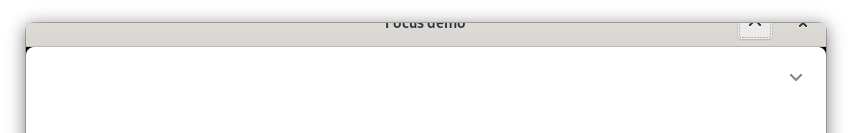
So there is no way right now to do it cleanly and without glitches, although you can get pretty close.
Fullscreen

I said above that Apostrophe uses two headerbars. Well, I lied! It uses three, the third one for fullscreen mode.
Like the titlebars drawn by X11 window managers, GtkWindow‘s titlebar area is hidden in fullscreen. At the same time, our HIG recommends to still have a headerbar in fullscreen, but to autohide it. The easiest way for apps to implement this is to have another headerbar inside a GtkRevealer in GtkOverlay in the window content area, that’s normally hidden and only shows up in fullscreen mode. Then it can be shown and hidden by application whenever wanted.
However, this means you have to have two (or more!) headerbars, or to reparent it from titlebar to the revealer when entering fullscreen and then back to titlebar when exiting it, like DzlApplicationWIndow from libdazzle does.
Showing content behind the headerbar
What, you were expecting a screenshot? Since the titlebar area is completely separate from the window, it’s impossible to show content behind it.
Similarly, things such as showing scrolling content behind titlebar, like macOS and Windows do, are impossible.
Window/titlebar split
All of these problems are caused by the fact titlebar is separate from the window. If that wasn’t the case, it would all be a lot simpler:
- For split headerbars and stack navigation you would be able to use a single box/stack/leaflet/deck spanning the whole window, no need to duplicate the hierarchy in the titlebar.
- Autohiding would be a matter of using
GtkRevealerand/orGtkOverlay, just like in fullscreen. - The headerbar wouldn’t be hidden in fullscreen, so it would be possible to reuse the widget without reparenting or duplicating it.
- Similarly, showing content behind the headerbar would be perfectly possible with just
GtkOverlay.
So, how do we eliminate the split? Obviously, it’s not an option for GTK3. There’s GTK4, but it would be nice to have something working in the meantime. This means libhandy.
HdyWindowHandle
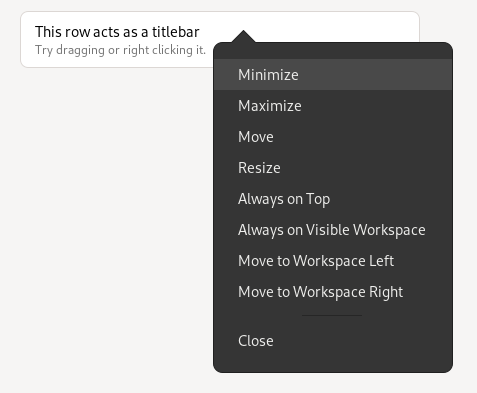
The first thing we need to have headerbar inside the window hierarchy is to make it act like a titlebar. GtkHeaderBar isn’t enough: while it has the overall layout and window controls, it doesn’t handle dragging, or right-click menu, or double click, or middle click. All of this is provided automatically for the titlebar widget, whatever that widget is, and that’s it.
To solve that, libhandy now has a HdyWindowHandle widget. It’s a GtkBin subclass that acts as a “titlebar area”. Dragging it will move the window, right clicking will produce a menu etc.
So, when a headerbar is used inside a window, it can be wrapped into a HdyWindowHandle and it will just work. It can also be used to easily make the whole window draggable. Or a random part of it for whatever reason.
HdyHeaderBar
However, the HdyWindowHandle has a downside of being easy to forget when creating a headerbar. If it’s not used, the window looks exactly the same, but the headerbar can’t be dragged. It’s especially easy to miss if you’re testing your app on a phone, where the window can’t be moved, or usually move windows while holding the Super key.
And it just so happened that (for unrelated reasons), libhandy has had a fork of GtkHeaderBar called HdyHeaderBar. It now features the same draggability and right/double/middle click handling as HdyWindowHandle, so can be used as is.
HdyWindow
One thing about the headerbars being in a separate area from the window content is that they can easily have round corners. While the window background can have round corners via CSS (and in fact that’s what elementary OS has been doing with the .rounded style class), nothing prevents the window content from overlapping them. This is true for the titlebar as well (see HdyTitleBar), but there’s a lot less chance of that happening.
However, if we want to display content behind the headerbar, or to autohide the headerbar, it’s pretty much guaranteed to happen.
One way to prevent that is to mask the corners. This guarantees nothing can ever overlap them. And that’s exactly what HdyWindow and HdyApplicationWindow are doing.
Coincidentally, GTK has no public API to inspect border-radius CSS property for each corner separately, so these windows also have round bottom corners.
They also draw a sheen on top of the window, which is normally on the headerbar. It looks the same way if a headerbar is used on top of the window, but still looks good if it’s hidden.
Limitations
However, the corners come at a cost: they cause an overhead when OpenGL is used. Normally GTK has a fast path for when nothing is overlapping OpenGL drawing (such as inside a GtkGLArea). However, masking corners requires a redirection, so the gains from that are negated.
On my machine the only place I was able to notice it is in GNOME Games running particularly “heavy” games on a workspace with lots of windows.
At the same time I wasn’t able to notice any differences with Web or Boxes when using HdyApplicationWindow.
Additionally, in maximized, tiled or fullscreen mode, or simply with border-radius: 0; there’s no need to mask anything, so there should be no difference compared to regular GtkWindow.
Future
These widgets have already landed in libhandy master, and can be seen in action in nightly builds of GNOME Games. However, there are some pieces of the puzzle missing right now.
While the same headerbar can be used in windowed and fullscreen modes, there’s no widget to show it next to the content in windowed mode like in a GtkBox, and on top of the content in fullscreen mode like in a GtkOverlay. Right now I have such a widget implemented in Games, but it will need to be in libhandy so that each application doesn’t have to reimplement it.
Currently HdyHeaderGroup only supports GtkHeaderBar, but not HdyHeaderBar, so for split headerbars you still have to use GtkHeaderBar and HdyWindowHandle.
Additionally, the headerbar in the window won’t automatically have .titlebar style class, so won’t pick up styles such as the .devel cog and gradient, so either everybody must manually add it, or HdyHeaderBar could have it by default.
And most importantly, it needs to be implemented for GTK4.
But meanwhile, enjoy freeform round windows!