We are laboring on getting Fedora Workstation 31 out the door next Month, with the beta release being made available last week. So here are some of the highlights of this upcoming release which I and the team hope you will enjoy. Many of these items I already covered in my June blogpost about Fedora Workstation 31, so if you read that one consider this one a status update as there will be some repeats.
Wayland improvements
Fedora has been leading the migration to Wayland since day one and we are not planning to stop. XWayland on demand has been an effort a lot of people contributed to this cycle. The goal is to only need XWayland for legacy X applications, not have it started and running all the time as that is a waste of system resources and also having core functionality still depend on X under Wayland makes the system more fragile. XWayland-on-demand has been a big effort with contributions from a lot of people and companies. One piece of this was the Systemd user session patches that was originally written by Iain Lane from Canonical. They had been lingering for a bit so Benjamin Berg took those patches on for this cycle and helped shepherd them over the finish line and get them merged upstream. This work wasn’t a hard requirement for Wayland-on-demand, but since it makes it a lot easier to do different things under X and Wayland which in turn makes moving towards XWayland-on-demand a little simpler to implement. That work will also allow (in future releases) us to do things like only start services under GNOME that are actually needed for your hardware, so for instance if you don’t have a bluetooth adapter in your computer there is no reason to run the bits of GNOME dealing with bluetooth. So expect further resource savings coming from this work over time.
Carlos Garnacho then spent time going through GNOME Shell removing any lingering X dependencies while Olivier Fourdan worked on cleaning up the control center. This work has mostly landed, but it is hidden behind an experimental flag (gsettings set org.gnome.mutter experimental-features "[...,'autostart-xwayland']") in Fedora 31 as we need to mature it a bit more before its ready for primetime. But we hope and expect to have it running by default in Fedora Workstation 32.
One example of something that was still requiring X that is now gone is the keyboard and mouse accessibility features in GNOME 3, which Olivier Fourdan got re-implemented and improved for this release. So if anyone out there reading this rely on the hover click accessibility feature then that is actually a lot nicer in Fedora Workstation 31. As seen in the screenshot below you now have this nice little pie animation filling up as it prepares to click which is a huge improvement over how it used to work.
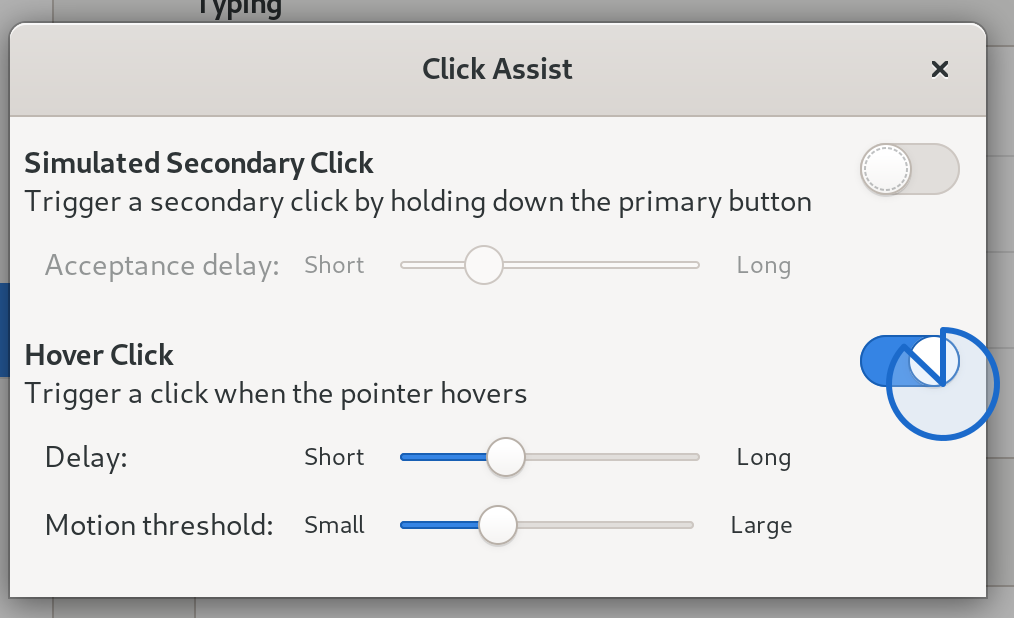
Click on hover in action
Another item we feel is an important part of reducing the need for XWayland is having Firefox running natively on Wayland. Martin Stransky and Jan Horak has been working tirelessly on trying to ensure Firefox works well on Wayland and in the Fedora 31 Beta it is running on Wayland by default. However there are a few bugs discovered that Martin and Jan are trying hard to fix atm so we can keep this default for the GA release, but if they miss the deadline we will ship the X backend version in F31 and then move to the Wayland version later on.
In Fedora Workstation 31 Wayland is still disabled by default if you use the Nvidia binary driver. The reason for this is due to lack of acceleration under XWayland, meaning that any application depending on GLX, like a lot of games, will just get software GL rendering with the binary NVidia driver. This isn’t something we can resolv on our own, Nvidia has to do the work since its their closed source driver, but we been discussing it regularly with them and we been told now that they are looking at the work Adam Jackson some time ago which was specifically aimed at helping them bring their X.org driver to XWayland. We don’t have a timeline yet, but it is being actively looked at and hopefully a proper date can be provided soon. I am actually running Fedora Workstation 31 using the NVidia driver myself at the moment on this laptop, and for those interested in helping dogfood this setup, in preparation for hopefully being able to enable Wayland on NVidia in Fedora Workstation 32, it is fairly simple thing to do. Under /usr/lib/udev/rules.d/ you find a file called 61-gdm.rules, just edit that file and comment out (#) the line that reads ‘DRIVER=="nvidia", RUN+="/usr/libexec/gdm-disable-wayland"‘ and you will revert to a standard setup where your standard session is a Wayland session, but with a x.org session available as a fallback. The more people that run this and report issues the better as it helps us make this rock solid before releasing it upon the world.
Atomic kernel modesetting
Jonas Ådahl has been hard at work this cycle on adding support for atomic mode setting. This work is not done, but the first parts of it has landed, but it has major long term advantages for us. I asked Jonas to provide a short description of the work and what it will eventually achieve as I don’t we articulated that anywhere else yet:
There are two ways for a display server to control the configuration and content of monitors – the old classic Kernel Mode Setting (classic KMS), and newer atomic Kernel Mode Setting (atomic KMS). The main difference between these two modes of operations is that with atomic KMS, the display server posts transactions containing configuration KMS that are then processed atomically by the kernel, while when using the classic KMS, the display server posts configurations command by command, where each monitor is configured by posting multiple commands. The benefits with atomic KMS are for example that the display server will up front know whether a configuration is valid (e.g. enough memory bandwidth), or that the display server can configure multiple aspects of the hardware atomically.
During the cycle leading up to Fedora Workstation 31 the foundations for how mutter (the window manager powering GNOME Shell) can make use of the new atomic KMS API was put in place. What was done was to introduce an internal transactional API for configuring monitors. This will eventually allow us to have much more control over how more advanced monitor features are utilized. For example it will be possible to place client windows directly in hardware overlay planes, meaning we can more often completely bypass full frame compositing when only the content of a single window changes. Another example for what this enables us to do is with color management; we will be able to do seamless switching between managing window color profiles using OpenGL and for instance gamma ramps. Yet another example of what this work opens the door for is framebuffer modifiers, which will among other things potentially result in higher performance with very high resolution monitors.
Finally an important aspect of the work done related to the new internal KMS API is that it aims to be thread safe, meaning eventually it will be possible to put KMS processing completely in a separate thread. This means that together with e.g. moving input device processing to its own thread it will be possible to get very short latency between mouse movement and the cursor
being moved on screen.
QtGNOME improvements
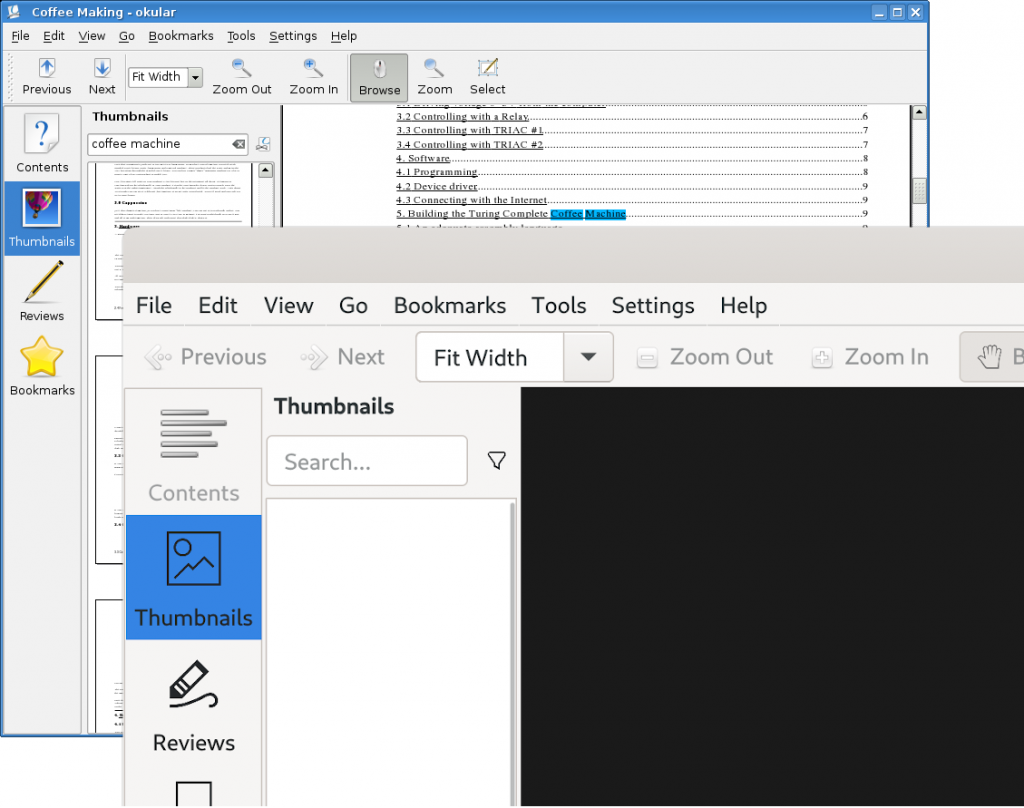
Jan Grulich has continued improved the QtGNOME module to make sure Qt apps integrate as well as possible into Fedora Workstation. His latest updates ensures that the theming keeps up to date with latest upstream changes in Adwaita, that we have a fully working dark theme, that accessibility theming work and that it works with Flatpaks. Below is a screenshot showing Okular running allowing you to see how the QtGNOME module affects the look and feel of Qt applications.
Firmware improvements
The LVFS firmware service keeps going from strength to strength. Richard Hughes presented on it during the Open Firmware Conference recently and was approached by a lot of vendors afterwards both thanking him and Red Hat for the effort, but also asking about getting more of their hardware supported. New vendors are coming onboard at rapid pace, for instance Acer joined recently and are planning to support more of their hardware on the LVFS going forward. It is also worth mentioning the GNOME Firmware tool that can now be downloaded from flathub and which works great on Fedora Workstation 31.
OpenH264 Greatly Improved
The much improved version of OpenH264 will be available soon for Fedora users. This new version adds support for the High and Advanced profiles of H264 which is what most videos found online or produced by your camera would be using. This means you can add H264 playback support to your Fedora Workstation without having to search online for 3rd party repositories like you have had to do up to now. We also are trying to ensure this will be usable by Firefox for video playback eventually. This was work we partnered with Endless, Cisco to hire the multimedia experts at Centricular to do, so another great example of cross company collaboration to bring improved functionality to the community.
Fedora Toolbox
Debarshi Ray has been working on many small improvements and better robustness for Fedora Toolbox going into Fedora Workstation 31. Fedora Toolbox for those not aware of it yet, is our tool to make doing development using pet containers simple and convenient, providing ease of use features on top of traditional container tools and integration with GNOME terminal and the GNOME Shell. The version shipping in F31 will be the last shell script based one as once Fedora Workstation 31 is out we will be going all in on rewritting Fedora Toolbox in Go, in preparation for future development and expansion. I strongly recommend trying it out as it will help open your eyes to the possibilities that using pet containers for development gives you. For instance you can easily set up a RHEL based pet container on your Fedora system to do development work that is mean to be deployed on a RHEL system or grab our special AI/ML development container for easy access to TensorFlow and similar tools.
Improved Classic mode
Another notable change in this release is the updates to GNOME Classic mode. GNOME Classic mode is a set of extensions to GNOME 3 that makes it look and behave a lot more like GNOME 2, which still has many fans out there. With this release we collected feedback from a group of Classic mode users and tried to improve the experience further, mostly be removing some remaining GNOME 3’isms that didn’t really fit the GNOME Classic user experience, like the overview and the hot corner. The session manager is now also easily accessible in the bottom corner. The theming also got cleaned up a little to remove the last bit of the ‘black’ GNOME 3 theming. That said I think it is important to remember that this is still GNOME 3 in the end, we are really just showcasing the power of extensions to tweak the user experience in quite fundamental ways here.
Improved GNOME Classic mode
Fedora Workstation is used all over the globe, but we have not been happy about how our support for picking languages other than English has worked so far. The thing is that if you choose one or more languages at install time, things tended to just work fine, but if you wanted to add a new language afterwards it required jumping onto the command line and figuring out how to install the needed langpacks. In Fedora Workstation 31 Sundeep Anand have worked hard to improve this, so if you choose a new language in the GNOME Control center in Fedora Workstation 31, the required langpacks should be installed automatically for you.
Fleet Commander
Fleet Commander 0.14.1 is out just in time for Fedora Workstation 31. Fleet Commander is a tool for doing large scale deployments of Fedora and RHEL workstations, allowing you to set system wide profiles. So for instance if you have a GNOME Shell extension everyone in your organization or a specific team inside your organization should have enabled, you can deploy a profile with Fleet commander ensuring that extension is enabled for those users. Basically any setting within GNOME can be set using this, including network configuration options. There is also support for Firefox and LibreOffice settings in Fleet Commander. The big feature addition of 0.14.1 is that Fleet Commander now can be used with Active Directory, which means that even if your company or university use Active Directory for their user management, you can now deploy Fedora and RHEL profiles without needing FreeIPA. Fleet Commander is pretty much finished at this point, at least as far as any piece of software can ever be finished. Oliver Gutierrez Suarez is working on finishing up some last bits of Firefox support currently, but we don’t have any major Fleet Commander items on his todo list after that, so if you been waiting to test it out there are on new major features you need to wait on anymore, it is all there. If you are doing large scale linux desktop deployments I definitely recommend checking out Fleet commander. You will find that Fleet Commander definitely makes Fedora a great choice for doing large scale Linux desktop deployments.
Pipewire
We are not doing a lot of changes to Pipewire for Fedora Workstation 31. Mostly some bugfixes and minor improvements to the video infrastructure it already provides in Fedora 30 for Flatpaks and web browsers. We are planning major changes for Fedora Workstation 32 though, where we in fact plan to ship Pipewire as a tech preview for both Jack and PulseAudio users. The way it will work is that the system will still default to PulseAudio, but we will provide either a script or a UI option to switch over to Pipewire (and back again). There is also a plan to have a core set of ProAudio applications available as Flatpaks for Fedora Workstation 32 tested and verified to work perfectly with Pipewire, the current apps planned to be included are Ardour, Carla, a2jmidid, Hydrogen, Qtractor and Patroneo, but if there is interested contributors joining the effort we could have even more. Then for Fedora Workstation 33 the idea is to ship with Pipewire as the default audio handler, but with some way for users to switch back to PulseAudio if they have a need. Not unlike how the setup is currently with Wayland and X.org in Fedora. Wim Taymans will also be attending the Sonoj conference in Cologne Germany at the end of October to discuss Pipewire with many members of the Linux ProAudio community and hopefully help prepare them for a future where Fedora Workstation is the perfect home for ProAudio users and developers.
Sysprof
Christian Hergert spent some cycles this round on improving the Sysprof tool as it was becoming clear that to keep improving GNOME Shell and general desktop performance going forward we needing better data and ability to find the bottlenecks. Tools like sysprof often ends up being the unsung heroes of the system, but as we continue improving the overall GNOME performance and resource usage of the next few years the revamped sysprof tool will be a big part of that story.
Much improved Sysprof tool
Silverblue
A lot of the items we work on are part of our vision around Silverblue, a Linux desktop OS built on the idea of an immutable core image. We often mention the theoretic advantage that such a setup with an immutable OS brings, but actually as I upgraded from F30 and F31 beta on my RPM based laptop (I got a separate machine where I run Silverblue) I hit the exact kind of issue that Silverblue can help us and our users avoid. What happened was that after my upgrade I suddenly had no Wayland session anymore, just the fallback X.org session. After quite a bit of fault searching I discovered that the reason for this was that I had been testing Valves ACO shader compiler on F30. These packages had a newer version number than the F31 packages and thus where not overwritten as part of the upgrade. Unfortunately the EGL package that came as part of that repository did not work well on F31 and thus the Wayland session failed. Once I did a distro sync and forced all packages to be the actual F31 versions things worked correctly, but it did illustrate the challenges with systems where different parts of the core can and will get updated at different times. With a single well tested core OS image these kind of problems will not happen. That said being able to test such things as ACO is valuable and useful and luckily OStree and Silverblue do offer functionality for installing such things in a clean and non-damaging way through what is known as package layering. When you install new packages like that on using package layering they will only last until your next reboot, after you reboot your back to a clean original state system. Of course if you really want to keep some experimental packages around there are other things you can do too, like overriding, but for simple testing like I did with ACO, package layering will provide you with a simple and safe way to do that.
We realize that Silverblue is a major change in how a Linux distro is ‘supposed’ to work, so we are taking our time with it to ensure we do it right and that we have made sure applications and tools work in a way that functions well on an immutable OS. So if you are interested I do recommend that you grab the Fedora 31 Silverblue image and give it a spin, but we are still working on polishing the experience so don’t expect it to be a seamless experience at this point in time. Of course as things like Flatpaks, Fedora Toolbox and a host of smaller issues get improved upon we do believe this will be such an overall improvement over an ‘old fashioned’ linux distro that you will be asking yourself why the Linux world didn’t do this years ago.
Improved performance
A lot of work has gone into improving the general performance of GNOME 3.34. The GNOME shell team has been very active and is a great example of a large numbers of developers working together from different backgrounds. So this release features a lot of great performance work by Daniel van Vugt from Canonical and by Georges Stavracas from Endless for instance. The Red Hat team has focused on providing patch review and feedback and working on bigger long term changes and enablers, like Christian Hergerts work on Sysprof, Jonas Ådahl work on atomic mode setting and Benjamin Bergs work on systemd-user session support. All in all I think you will find that Fedora Workstation 31 with GNOME 3.34 provides a faster and smoother experience, an experience we will continue to build upon going forward as some of these long term efforts starts paying off.

Performance is better than ever
Summary
So this has been a roundup of some of the core items you should look forward to in Fedora Workstation 31. There are other items coming too in this release, like the Miracast GNOME Network Display application that Benjamin Berg has written, more Fedora Flatpaks available than ever before and more. We also have a lot of interesting items coming up in Fedora Workstation 32 like Bastien Noceras work improving low memory handling. So stay tuned.